Education
Explore the Value and Importance of P20 Education Councils!
P20 Education Councils provide a knowledge pipeline for students
Posted January 10, 2020 Reviewed by Hara Estroff Marano
What is a P20 Education Council? (Preschool through Graduate School)
A P20 Education Council is a local partnership organization whose purpose is networking and linking a relevant continuum of important information from preschool through university and into careers for our evolving 2020 workforce. This article explores the reasons, structure, partners, and plan that can bring together a major communication vehicle for achieving the important goal of informing, advising, and helping students progress in education.
P20 Education Councils are structured as a vertical pipeline vehicle for student advising, counseling, guidance, and information. P20 Education Councils promote communication, agreements, and opportunities between school districts, colleges, universities and industries to facilitate student advancement and certificate and degree program progress by smoothing out the present disconnected communication system of education from preschool through graduate school and into the workforce.
Having the right information is the key to student advancement.
P20 Education Councils are beginning to emerge nationwide. P20 Education Councils facilitate collaboration between local segments that include preschool networks, charter school networks, elementary and middle school districts, high school districts, unified school districts, community college districts, independent colleges, state colleges and universities, military bases, representatives of industry, and the press. Networks of P20 Education Councils can become increasingly important for advising, counseling, and communication of possibilities. One special purpose of a P20 Education Council is to foster clear communication in solving the discontinuity between our education sectors.

Community colleges are the natural leadership partner in fostering this partnership movement. A council can also be a vehicle for enabling a wide network of leaders from cooperating segments to work together through the council in getting needed information to students. The way community colleges are organized in the United States offers a natural leadership partner and coordinating network to help link P20 Education Council members.

One example of a successful P20 Education Council is in Ventura County, California. I helped develop this council while serving as Chancellor of the Ventura County Community College District. It is one of many successful P20 Education Councils now dotting the nation.
P20 Education Councils are evolving simultaneously with new 21st century occupational and career specialties. While each segment is an important partner, the community college is central to the emergence of the P20 Education Council networks for specific reasons. Working together with local universities, school districts, industry, and military participants, the local community college is a unique hub in areas it serves.
There is now a community college in driving distance of every American, so a national leadership network is already in place. Articulation agreements for dual enrollment, online program offering, credit transfer, counseling and advisement, communication, scholarships, financial support, and consistent vertical articulation can all come together and effectively share through the P20 Education Council model.
Natural partners for success include community college leadership in pulling preschools, K-12 school districts, colleges, and universities together in an organized for all students. With assistance from the P20 Education Council, students will have better access to the counseling and knowledge needed to make informed decisions to successfully climb the education ladder of career choice in all-collar categories of opportunity.
New-Collar jobs are harbingers of the 2020 workforce.
In 2016 IBM’s CEO Ginni Rometty coined the term “ new collar” jobs in an open letter to President-Elect Donald Trump (Lovelace, 2016). Congress subsequently established a milestone for the future in approving the “New Collar Jobs Act” in July 2017. Narrow and little known at this moment, the act provides special scholarship funding only in cybersecurity. It reinforces that the new-collar idea is an important rung on the advancement ladder, highlighting new collar opportunity that helps us see and plan. The expanding possibilities and implications of new-collar jobs are real and dramatic.
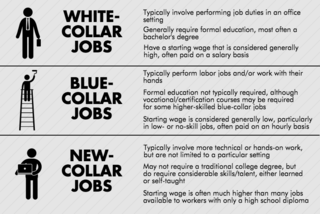
Historically, attributing colors, such as white-collar, blue-collar, pink- collar, and other colors, to job categories has provided identification of various categories of the workforce. "New collar” signals an important advancement, helping to clarify new career and workforce opportunities. New-collar jobs signal that the world of work has moved from post-industrialism through technology into an exciting, dramatic future on many fronts needing exploration, definition, and articulation. Students need up-to-date information about the opportunities from early grades forward.
The gig economy.
Cloud computing technicians, database managers, cybersecurity analysts, and user-interface designers are examples of the myriad new IT jobs that have emerged as we advance the gig economy. University and community college technology and engineering programs are providing employees for the pioneering edge of many of these new-collar opportunities. In addition, liberal arts and graduates in other majors have a variety of new-collar options to consider and pursue. New AA degree programs, new BA degrees, new graduate programs and a variety of certificates are coming online offering bridges to the new career opportunities.

The substantial number of new-collar careers is redefining the world of work. Students advancing in their education need clear information and planning to help them work toward opportunities that will make them successful and happy in work and life.
Foundations for work in the future.
Energy, synthetic biology, biomedical advancements, increasingly smart machines, quantum computing, and innate human competitive drive are igniting transformative opportunity and signaling the prospect of future jobs unlike those of which we are presently aware. Renewable energy is rapidly getting cheaper. More efficient solar panels and wind turbines are growth segments. Solar and wind are fields that are stimulating a boom in productivity. Synthetic biology and human genome manipulation are enabling the manipulation of genes leading to new biological materials advancing our ability to dramatically alter and manage DNA.
Our future is rapidly moving through new architectures, scientific breakthroughs, and 21st-century opportunities in robotics. Many new-collar jobs are powered by quantum computing, neuromorphic chips, and other trends. Advances are bringing new machines, new computer coding languages, algorithms, and strategy breakthroughs into the marketplace.
While online everything is expanding, malls are being rethought and reoriented, leading to new ways to make them successful. Each of these new workforce developments foreshadows our fast-paced continuum of innovation in commerce, science, health care, government, education, and entertainment, each of which has implications for new-collar jobs, present occupations and significant change in our world of work. Expansion is propelled by pressures for innovation generating a variety of all levels of new-collar, white-collar, blue-collar, pink- and other-collar jobs and careers. New jobs are now on earth, increasingly in space, and in virtual reality environments. It's not even possible yet to name some of the many careers on and beyond the occupational and professional horizon.
Examples abound.
In space, tourism is now opening new vistas. Sir Richard Branson has announced Virgin Galactic, which will be one of the first public companies with a space agenda listed on the New York Stock Exchange. NASA announced a public-private partnership with Elon Musk’s Space X to expand commerce in space. These are more good examples of new emerging industries that that will operate on earth and in space as well.
In our new collar area, virtual reality jobs using VR goggles, headphones, and haptic suits now allow you to move your arms, walk around, and speak to avatars that answer back.
Recently, I was impressed by the virtual reality tours at the Shoah Holocaust Museum housed at the University of Southern California. In medicine, remote surgery has become one of the most dramatic areas of advancement. In addition, all types of sports will also boom because of innovations in augmented and virtual reality. Methods of construction, transportation, hospitality, medicine, and diagnostics in all fields offer myriad possibilities for new types of jobs and careers.
A large percentage of children entering primary school today will grow and develop into careers and job types that don’t exist today.
Universities, community colleges, high schools, middle schools, elementary schools, and preschools are a continuum of rungs on the career and work-life ladder. My conclusion is that the P20 Education Council idea, driven by community colleges and other key segments, will become increasingly important for purposes of articulation, communication, and organization.
A large percentage of children entering primary school today will grow and develop into careers and new job types that don’t exist today. Universities, community colleges, high schools, middle schools, elementary schools, and preschools are a continuum of education rungs on life’s career and work-life ladder. My conclusion is that the P20 Education Council idea, driven by community college leadership and leaders from the other key segments, is increasingly important for purposes of organization, articulation, and communication to students and employers.
Summary
The future is coming toward us. It is important that we improve educational opportunities for all students and help shape the future.
My recommended approach includes working with community colleges to provide coordinating leadership in establishing a nationwide network of P20 Education Councils to share information and provide guidance about opportunities. Organizing a local P20 Education Council network involves including active council members from preschools, K-6, K-8 and unified K-12 school districts; local, state and independent colleges and universities; military installations; industry leaders; press; and government leaders.
Future articles will discuss needs, organizational structures, networks and criteria for successful launch and operation of P20 Education Councils led by one of the strategically located 1,000 community colleges in our nation. A continuum of understanding and communication is an educational imperative for our students. This is an approach that can work. All the pieces are in place. What needs to be done is to put them all together. Providing information for students through a P20 Education pipeline that informs, educates, provides articulation, guidance and coaching about jobs, careers, workforce opportunities and lifetime networks is a good place to start.
Please email suggestions or comments to: Bernie@LuskinInternational.com
Special thanks to Toni Luskin, Ph.D., for editorial and publishing assistance.
Luskin Learning Psychology Series, No. 48
References
References:
Lovelace, Jr., B. (Producer). (2016, 01-08-20). IBM CEO Rometty in Letter to Trump: Help Secure "new collar" IT jobs. [Education] Retrieved from CNBC.com
Luskin, B.J. (2011). Legacy of Leadership. Washington, DC: W.K. Kellogg Foundation.
Luskin, B.J. (2019) Invisible in Plain Sight, Psychology Today, The Media Psychology Effect.
Luskin, B.J. (2019) 5G Technology Explodes New Careers in Forensic Media, Psychology Today, The Media Psychology Effect
Donnelly, Elaine K., Regional P20 Councils: Addressing the Education Pipeline Through Regional Learning and Cross-Sector Collaboration, Dissertation, University of Massachusetts, 2017
Luskin, T.T., Luskin, B.J. (2000). Worklife Learning: The New Mantra of .com and .edu. The Heller Report, Five, number seven (January 2000), 50. ADDIN EN.REFLIST




