Memory
Enhance Memory with the "Production Effect"
Do something with new learning—right away!
Posted December 15, 2017
When you encounter new information and want to remember it, the formation of a memory is enormously affected by what happens immediately afterward. The most common problem is that you think of something else and that something else erases what you just learned from your working memory “scratchpad” before it has time to set up in long-term memory.
The way to avoid this problem is to do something with the new learning right away. Memory scientists often call this a “production effect." That is, if you produce something from the new learning right away, it not only reduces interfering distractions but also strengthens the encoding and speeds up memory formation into lasting form. Common production activities might include using the new information in a new way, to apply it in some kind of activity, such as solving a problem. This option is not always available, but there are other approaches, such as hearing the same information at the same time you read or see it. The most common production method may be taking handwritten notes during the presentation of the new information.
A recent study has compared the effects of silently reading, hearing somebody else read aloud, hearing a recording of one's self reading aloud, and actual reading aloud in real time as one learns. The last two groups tested to see if the actual mouth and tongue movements involved in reading aloud at the time of reading seems to have any effect. It does.
The study divided 75 college students into these four groups in which they participated in two 15-minute sessions separated by two weeks. In the first session, they read a list of 160 words presented one at a time on a computer screen. They were to see each word and say it aloud into a microphone. They were not told why they were recording the sound of the words nor told what was to happen in the return session two weeks later.
In the follow-up session, students were randomly presented 20 of the words from the first session, according to the four groups (read silently, hear another say the words, hear the self-recording, or actively say each word). Immediately after this, students took a self-paced recognition test to identify how many of the study words were recognized.
Upon testing, a clear gradient of improvement was evident with increased production effect. That is, poorest recognition occurred with silent reading and best recognition occurred with actively saying the words.
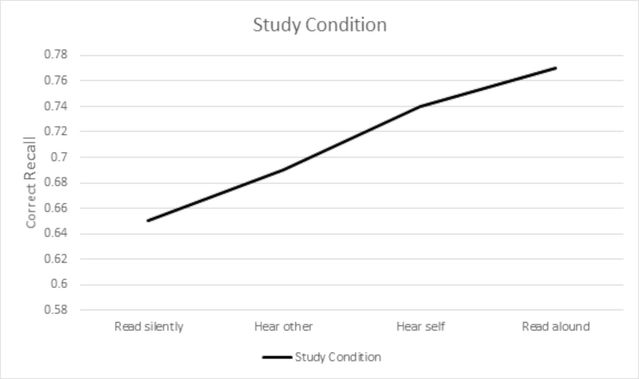
Why is reading aloud more effective than hearing yourself or others reading? The authors concluded that the self-reference and self-control over speaking produces more engagement with the words. The deeper the engagement, the better the memory. They also attribute the self-referencing as the explanation for why rehearsal helps memory formation. We do it ourselves and do it in our “mind’s ear.”
I think there are other implications of these findings. Other research establishes that rehearsal should require forced recall, rather than just passively looking over the study material. The data shown here suggest that rehearsal would be even more effective if we forced ourselves to recall by stating the material out loud.
Note that this study measured recognition memory. This is similar to what students do when taking a multiple-choice test: They are given prompts to see if they recognize the correct choice. This is much less demanding than requiring the student to generate the right answer “from scratch,” as in a fill-in-the-blank type of question. Open-ended testing might reveal an even greater benefit from production effects. Optimal benefit would probably come from reading aloud from notes that the student took at the time of initial exposure to new information.
References
Forrin, N. D., and MacLeod, C. M. (2017) This time it’s personal: the memory benefit of hearing oneself. Memory. DOI: 10.1080/09658211.1383434.


